Simulate a simple galaxy with surveycodex and GalSim¶
In this tutorial, we will see how we can use the survey parameters in surveycodex to create a simple elliptical galaxy with galsim. The galaxy will be convolved with a optical+atmospheric component PSF, include background and noise, and use the r-band filter of the LSST survey.
Please note that galsim is not a surveycodex dependency, so it must be installed
separately to follow this guide. See here
for galsim installation instructions.
To draw the image at the end of the tutorial, matplotlib will also need to be installed separately.
First, we import galsim and necessary functions from surveycodex.
import galsim
import surveycodex
from surveycodex import get_survey
from surveycodex import utilities
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
Then, we specify the survey and filter from surveycodex we will use. Along with galaxy parameters.
# surveycodex survey and filter.
LSST = get_survey("LSST")
r_band = LSST.get_filter("r")
# galaxy model parameters
mag = 22.0 # ab
e1 = 0.2
e2 = 0.2
hlr = 1.2 # arcsecs
Now we create a galaxy model and shear it.
# get flux from magnitude using surveycodex for LSST r-band.
total_flux = mag2counts(mag, LSST, r_band)
# get only the value of flux in desired units.
total_flux = total_flux.to_value('electron')
# simple gaussian galaxy with ellipticity
gal = galsim.Gaussian(flux=total_flux, half_light_radius=hlr)
gal = gal.shear(e1=e1, e2=e2)
Now we create a PSF, first the atmospheric component.
fwhm = r_band.psf_fwhm.to_value("arcsec")
atmospheric_psf_model = galsim.Kolmogorov(fwhm=fwhm)
Then, the optical component.
effective_wavelength = r_band.effective_wavelength.to_value("angstrom")
obscuration = LSST.obscuration.value
mirror_diameter = LSST.mirror_diameter.to_value("m")
lam_over_diam = 3600 * np.degrees(1e-10 * effective_wavelength / mirror_diameter)
optical_psf_model = galsim.Airy(lam_over_diam=lam_over_diam, obscuration=obscuration)
The full PSF is the convolution of both components.
psf = galsim.Convolve(atmospheric_psf_model, optical_psf_model)
We convolve it with the galaxy model
conv_gal = galsim.Convolve(gal, psf)
Finally, we add noise and background:
# retrieve the sky level using surveycodex.
sky_level = utilities.mean_sky_level(LSST, r_band).to_value('electron')
# add noise and background to image.
pixel_scale = LSST.pixel_scale.to_value('arcsec')
generator = galsim.random.BaseDeviate(seed=0)
noise = galsim.PoissonNoise(rng=generator, sky_level=sky_level)
image = conv_gal.drawImage(nx=53, ny=53, scale=pixel_scale)
image.addNoise(noise)
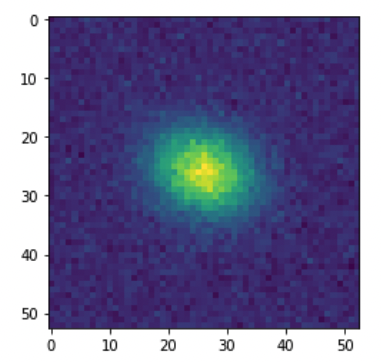
Now image.array can be plotted to see the galaxy that was produced.
plt.imshow(image.array)
We get the following image: